

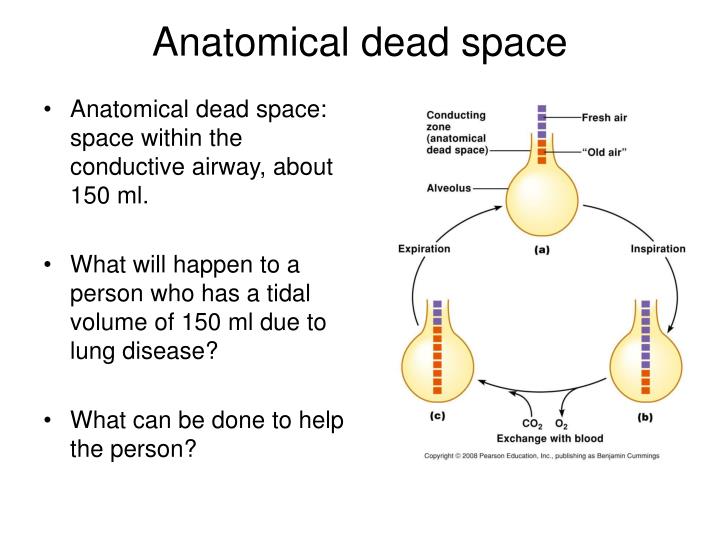
Even though one end of the tube is open to the air, when one inhales, it is mostly the carbon dioxide from expiration. Although the amount of gas per minute is the same (5 L/min), a large proportion of the shallow breaths is dead space, and does not allow oxygen to get into the blood.ĭead space can be enlarged (and better envisaged) by breathing into a long tube. ten 500 mL breaths per minute) is more effective than taking shallow breaths quickly (e.g.
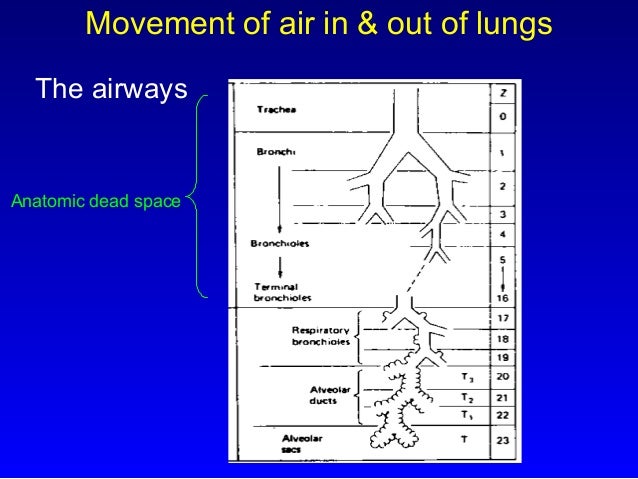
About a third of every resting breath is exhaled exactly as it came into the body.īecause of dead space, taking deep breaths more slowly (e.g. Not all the air we breathe in is able to be used for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. In adults, it is usually in the range of 150 mL. In physiology, dead space is air that is inhaled by the body in breathing, but does not partake in gas exchange. Risk calculators and risk factors for Dead spaceĮditor-In-Chief: C. US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Dead spaceĭirections to Hospitals Treating Dead space Ongoing Trials on Dead space at Clinical Articles on Dead space in N Eng J Med, Lancet, BMJ


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
